Revolutionary guidelines redefine analysis of bacterial shotgun metagenomic data
In an effort towards optimising the study of microbial ecosystems, a review article titled "Field and laboratory guidelines for reliable bioinformatic and statistical analysis of bacterial shotgun metagenomic data" authored by Assistant Professor Ostaizka Aizpurua and colleagues has just been published, providing a robust foundation in future metagenomics studies.
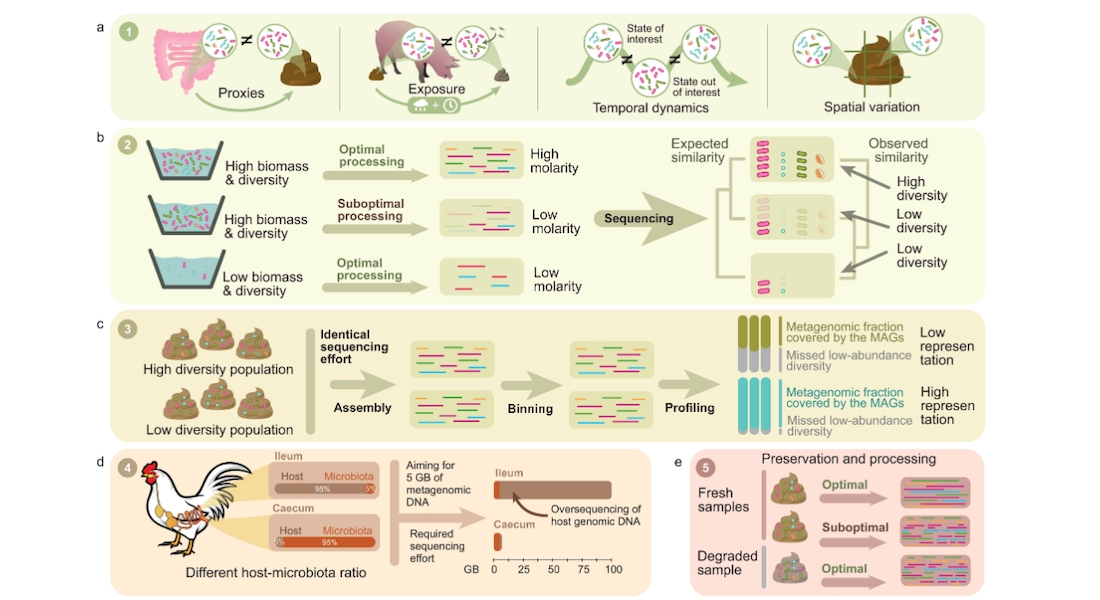
From fieldwork to bioinformatics
The study delves into the field of shotgun metagenomics, an increasingly cost-effective method for characterising microbial communities in both environmental and host-associated settings. Recognising the interplay between microbiomes and the demanding analytical techniques, the authors examine 15 critical aspects spanning fieldwork, laboratory protocols, and bioinformatic procedures, all important steps for hologenomic research.
These considerations include fundamental sample properties, study design, and strategic decisions made in the laboratory. The research illuminates the intricate links between field and laboratory procedures and their impact on subsequent bioinformatic and statistical data processing, as well as the interpretation of results.
A solid foundation in metagenomic studies
The authors of the study, provides means to identify potential pitfalls and present mitigation strategies to either circumvent or reduce their impact in metagenomic studies. By doing so, they establish a robust foundation for ensuring the reliability and representativeness of results derived from bacterial shotgun metagenomic analyses.
“With this work we want to raise awareness about the many ways in which we can introduce biases into our data, and the effects such distortions can have on our result interpretation. This is especially critical when sample processing is externalised to companies and control over sample processing steps is lost. Therefore, we hope these guidelines will help researchers to better design their studies and data generation strategies, to produce highest-quality data with which to untangle host-microbiota interactions” says Assistant Professor Ostaizka Aizpurua.
A new era of precision and rigour
The anticipated impact of these guidelines extends across the scientific community, promising to empower data scientists in appropriately handling and interpreting their data. Additionally, it equips field and laboratory researchers with actionable strategies to enhance the quality and comparability of their research outcomes.
In an era where understanding microbial ecosystems holds immense promise for applications ranging from healthcare to agriculture, these guidelines are much needed. Institutions and researchers alike are encouraged to integrate these protocols into their practices, driving forward a new era of precision and rigour in microbiome research underpinned by a solid foundation of reliable and robust scientific methodology.
Read the publication in Critical Reviews in Biotechnology here.
Contact
Assistant Professor Ostaizka Azipura
